Introduction
In the world of investing, dividends are often seen as a sign of a company’s financial health and its commitment to returning value to shareholders. The Dividend Payout Ratio, a key metric in assessing a company’s dividend policies, provides invaluable insights into how much income a company returns to its shareholders relative to its total net income.
In this article, I have shared a deep understanding of the Dividend Payout Ratio, its calculation, significance, and much more.
Table of Contents
What is the Dividend Payout Ratio?
The Dividend Payout Ratio (DPR) is a financial metric that helps investors determine the proportion of earnings a company pays out to its shareholders as dividends. This ratio is important for assessing a company’s financial stability and its approach to managing profits—whether they prioritize reinvesting in the business or returning cash to shareholders.
The formula for Calculating the Dividend Payout Ratio
The formula for the Dividend Payout Ratio is straightforward:
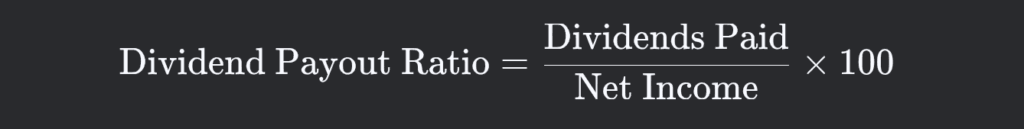
This calculation gives the percentage of earnings distributed as dividends.
What is the Importance of the Dividend Payout Ratio?
Understanding the DPR is essential for both new and seasoned investors for several reasons:
- Investment Decisions: It helps in making informed decisions about whether to invest in a company based on dividend income expectations.
- Company’s Financial Health: Provides insights into a company’s financial stability and profitability.
- Earnings Management: Indicates how well a company manages its earnings between reinvestment in the business and rewarding shareholders.
How to Interpret Dividend Payout Ratios?
- High Dividend Payout Ratio: Typically indicates that a company is mature, generating sufficient earnings to distribute a substantial portion as dividends. However, it might also suggest limited growth opportunities.
- Low Dividend Payout Ratio: Suggests that a company is reinvesting more of its profits back into the business, which might be typical for growing companies that are expanding operations, developing new products, or paying down debt.
Dividend Payout Ratio vs. Dividend Yield
While the Dividend Payout Ratio focuses on the percentage of earnings paid to shareholders as dividends, the Dividend Yield tells investors how much they are earning on their share price. Understanding both metrics provides a comprehensive view of a company’s dividend attractiveness.
Try out our calculator to understand more about dividend yield:- Dividend Yield Calculator.
ALSO READ:- How to Identify High-Dividend-Yield Stocks in India?
Analyzing Dividend Payout Ratios
Case Studies and Examples
Let’s consider two hypothetical companies:
- Company A has a high Dividend Payout Ratio of 80%. This might be appealing to investors looking for steady income.
- Company B has a low Dividend Payout Ratio of 20%, which might attract investors who are interested in growth and capital gains.
Industry Trends
Different industries have distinct norms for Dividend Payout Ratios. For instance, utilities often have higher ratios due to steady earnings and limited expansion opportunities, while tech companies may have lower ratios due to high growth prospects and reinvestment needs.
Significance of Dividend Payout Ratio for Investors
For investors, understanding the DPR is essential for making informed investment decisions. It helps them determine the sustainability of a company’s dividend payments. A consistently high dividend payout ratio that exceeds a company’s earnings may raise concerns about the company’s ability to maintain such payouts in the long term, potentially leading to cuts in the future.
Conversely, an appropriately balanced or moderate payout ratio indicates a company is capable of rewarding its shareholders while also investing in its future growth. Investors often look at the DPR alongside other financial metrics, such as the company’s earnings stability and growth prospects, to gauge the level of risk associated with an investment and its potential for long-term wealth generation.
Challenges and Limitations of the Dividend Payout Ratio
While useful, the DPR has its limitations. For example, it does not account for companies with negative earnings or those that pay dividends despite a loss. Moreover, this ratio can fluctuate widely for companies with volatile earnings, making it less reliable in such contexts.
Conclusion
The Dividend Payout Ratio is more than just a number; it is a reflection of a company’s priorities, stability, and outlook on growth. By understanding and interpreting this ratio wisely, investors can make more informed decisions, balancing the pursuit of income with growth potential.
This comprehensive analysis of the Dividend Payout Ratio provides investors with the knowledge needed to evaluate potential investments critically and strategically. As markets evolve and companies change their financial strategies, the DPR will continue to be a valuable tool in the investor’s toolkit.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute investment advice. Please consult a financial advisor before making any investment decisions.